Disease characteristics
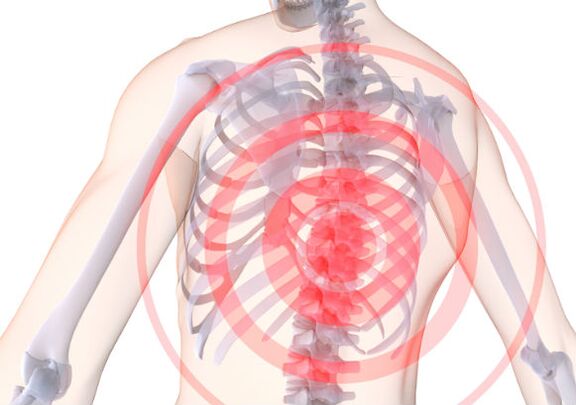
According to ICD-10, this disease belongs to the "dorsal disease" group with code M-42, localization.
reason

- excessive physical activity;
- Work involving lifting heavy objects;
- forcing uncomfortable positions for long periods of time;
- Congenital spinal curvature and acquired postural disorders;
- Incorrect diet;
- overweight;
- age-related changes;
- Metabolic problems.
extent and symptoms
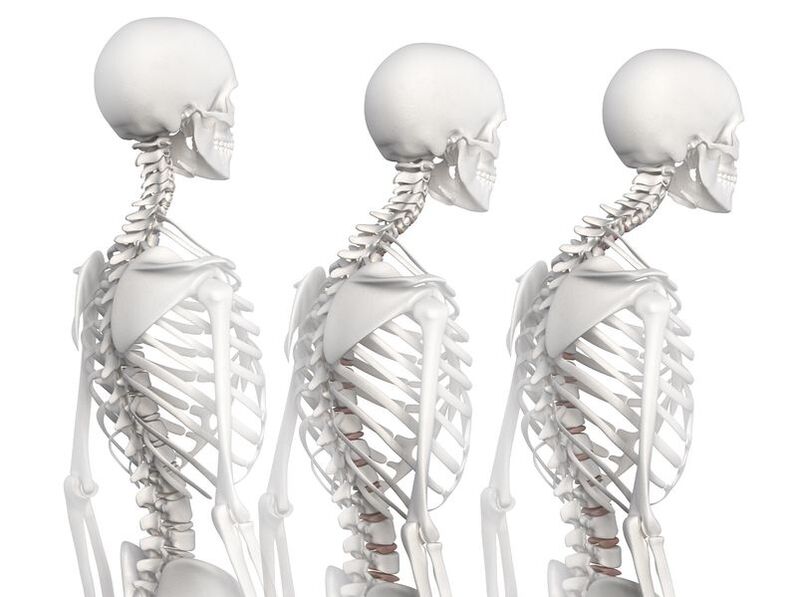
first level In the first stage, the elasticity (stiffness) of the disc and its height decrease. Possible sign of protrusion (bulging) of the annulus fibrosus (hard shell with a semi-fluid core). The cartilage tissue of the vertebrae becomes denser. Pain in the form of "low back pain" may occur during sudden movements or after remaining in one position for a long time. dosago- Characteristic symptoms of this stage. It manifests as sudden severe pain in the chest. It often occurs when a person stands up (difficulty breathing). back pain- Mild, non-sharp pain. It appears gradually and usually lasts 2 to 3 weeks. The condition can get worse after a sudden bend or physical exertion. Back pain is accompanied by muscle tightness and limited movement. The pain will lessen after a short walk. Also at this stage, neurological symptoms are also recognized: - A "pins and needles" sensation on the surface of the legs, abdomen, and chest;
- Numbness or tingling in certain areas of the skin;
- Gastrointestinal dysfunction.
second degree The height and elasticity of the intervertebral disc are further reduced. The thoracic spine becomes unstable and the annulus fibrosus develops cracks. Painful feeling: - Chest appears after overexertion or physical exertion;
- in upper back;
- when raising arms;
- While breathing (inhaling and exhaling).
Phantom pain in the heart area and intestinal dysfunction may also occur. Three degrees The formation of intervertebral hernia continues. Abdominal and back pain, intercostal neuralgia (may be aggravated by breathing, sudden movements, and coughing). One of the symptoms of osteochondrosis is cough. The overall mobility of the spine is reduced, the diaphragm is squeezed, and there is a feeling of lack of air. A severe dry cough is especially dangerous because the vertebral arteries are located in the neck. If compressed, there is a risk of ischemia and stroke. Level 4 In stage four, the disc no longer acts as a shock absorber. The spine loses its mobility. May pinch blood vessels and nerves. Bone tissue is susceptible to damage.
diagnosis
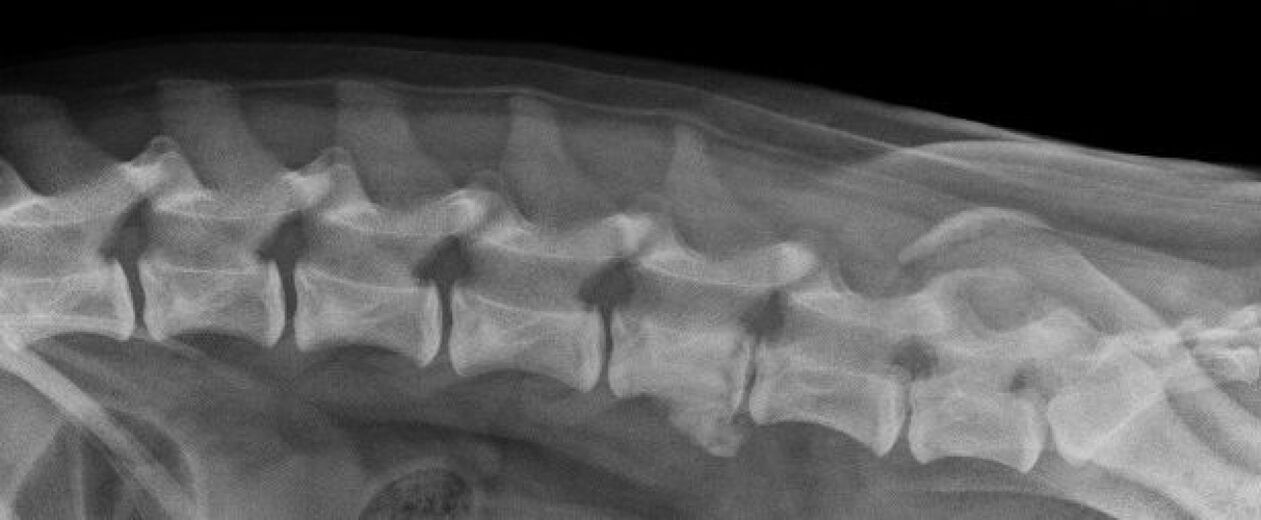
- ultrasound;
- X-ray;
- MRI;
- Blood analysis.
traditional treatment
- chondroprotectant. This is a group of drugs used to restore joint cartilage. The basis of most products are active substances - glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate.
- Antispasmodics and muscle relaxants.Drugs that reduce muscle tone. By acting on receptors in this way, they relieve unhealthy muscle tension that causes pain and cramps.
- painkiller.Reduces symptoms of disease - inflammation and pain. These drugs work by blocking the synthesis of certain enzymes.
- Vitamin therapy.The most common are vitamins A, B, D, C, and E, which restore cartilage tissue, strengthen the immune system, and have anti-inflammatory effects.
- massage.Patients with this condition need to undergo restorative massage sessions at least 2 times a year. This surgery is usually not performed during an exacerbation of the disease. The procedure improves blood circulation, relieves fatigue and muscle pain, and enhances muscle tone. The course lasts for a quarter of an hour and the duration of the course is 11-16 programs.
- Reflexology.Special techniques act on acupoints. This method is effective when combined with other methods.
- Exercise therapy.The disease is characterized by muscle underdevelopment and joint stiffness. A specially selected set of exercises (physical therapy) will help eliminate these symptoms. The first lessons should be conducted under the supervision of an experienced coach, followed by independent gymnastics. Regular training is very important.
treatment at home
- Nutrition
To improve the condition, you need to eat correctly: 6-7 meals a day, reduce salt intake, introduce vegetables and fruits, and natural cartilage protectants (jelly, aspic) into the diet. Additionally, it is important to maintain an active lifestyle and avoid any type of overload. - berry tea
Systemic consumption of berry tea as well as wild strawberry leaf tea reduces thoracic osteochondrosis. Place a tablespoon of the plant in a glass, add hot water and brew. It is recommended to drink at least two glasses of this drink per day (after meals). - potatoes and honey
Grated potatoes mixed with liquid honey can relieve pain and reduce inflammation. Apply the composition to the painful area for 30 minutes.






































